Summary for survivin (NES ID: 123)
Full Name
Apoptosis inhibitor survivin UniProt
Alternative Names
Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 5 (BIRC5), Apoptosis inhibitor 4 (API4, IAP4)
Organism
Homo sapiens (Human)
Experimental Evidence for CRM1-mediated Export
LMB Sensitive, Binds CRM1, Inhibit or inhibited by other CRM1 cargos Ref.1The Survivin-Crm1 interaction is essential for chromosomal passenger complex localization and function., Knauer et al., EMBO Rep, 2006 Ref.2Nuclear export is essential for the tumor-promoting activity of survivin., Knauer et al., FASEB J, 2007 Ref.3CRM1-mediated nuclear export determines the cytoplasmic localization of the antiapoptotic protein Survivin., Rodriguez et al., Exp Cell Res, 2002 Ref.4Separating the anti-apoptotic and mitotic roles of survivin., Colnaghi et al., J Biol Chem, 2006 Ref.5Homodimerization antagonizes nuclear export of survivin., Engelsma et al., Traffic, 2007
Mutations That Affect Nuclear Export
*highlighted yellow in the full sequence
L96A/L98A, F93P/L96A/L98A, 89VKKQFEELTL98 by Deletion, L98E/F101A/L102A Ref.1The Survivin-Crm1 interaction is essential for chromosomal passenger complex localization and function., Knauer et al., EMBO Rep, 2006 Ref.2Nuclear export is essential for the tumor-promoting activity of survivin., Knauer et al., FASEB J, 2007 Ref.4Separating the anti-apoptotic and mitotic roles of survivin., Colnaghi et al., J Biol Chem, 2006 Ref.5Homodimerization antagonizes nuclear export of survivin., Engelsma et al., Traffic, 2007 Mutations That Affect CRM1 Binding
*shown as red residues in the full sequence
L96A/L98A, L98E/F101A/L102A Ref.2Nuclear export is essential for the tumor-promoting activity of survivin., Knauer et al., FASEB J, 2007 Ref.1The Survivin-Crm1 interaction is essential for chromosomal passenger complex localization and function., Knauer et al., EMBO Rep, 2006 Ref.4Separating the anti-apoptotic and mitotic roles of survivin., Colnaghi et al., J Biol Chem, 2006 Functional Export Signals
*shown as underlined residues in the full sequence
89VKKQFEELTLGEFLKL104 Ref.1The Survivin-Crm1 interaction is essential for chromosomal passenger complex localization and function., Knauer et al., EMBO Rep, 2006 Ref.2Nuclear export is essential for the tumor-promoting activity of survivin., Knauer et al., FASEB J, 2007 Ref.4Separating the anti-apoptotic and mitotic roles of survivin., Colnaghi et al., J Biol Chem, 2006 Ref.5Homodimerization antagonizes nuclear export of survivin., Engelsma et al., Traffic, 2007 Secondary Structure of Export Signal
α-helix (residues 100-140)
Other Residues Important for Export
Unknown
Sequence
Show FASTA Format
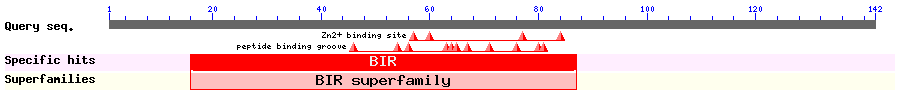
Show Domain Info by CDD
Show Secondary Structure by PSIPRED
Show Conservation Score by AL2CO
10 20 30 40 50 60MGAPTLPPAW QPFLKDHRIS TFKNWPFLEG CACTPERMAE AGFIHCPTEN EPDLAQCFFC70 80 90 100 110 120FKELEGWEPD DDPIEEHKKH SSGCAFLSVK KQFEELTLGE FLKLDRERAK NKIAKETNNK130 140KKEFEETAEK VRRAIEQLAA MD
3D Structures in PDB
Comments
The multiple functions of Survivin include inhibiting apopotosis and regulating cell division. Survivin is almost not detectable in adult human cells but overexpressed in most cancers. Survivin is a homodimer in solution and has an N-terminal BIR domain and a C-terminal coiled-coil domain (single long alpha-helix). In tumor cells, Survivin is found in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Overlapping NESs in Survivin were identitied by several labs: 1) Knauer et al identified residues 89-98 as NES. deletion of 89-98 and mutations L96A/L98A mislocalized Survivin and abolished CRM1 binding. 2) Colnaghi et al suggested 96-104 as NES. L98A mutant survivin is no longer cytoplasmic but still binds CRM1. 3) Engelsma et al reoports that 89-98 is a weak NES and the complete signal resides within 84-109 but only in monomeric Survivin. Mutations F101A/L102A disrupted the dimer and increased CRM1 affinity significantly while additional L98A completely abolished CRM1 binding. Hydrophobic residues within 89-98 (that match NES consensus) are not accessible in structures of survivin dimer, survivin-borealin and survivin-borealin-INCEP complexes.
References
[1]. "The Survivin-Crm1 interaction is essential for chromosomal passenger complex localization and function."
Knauer SK, Bier C, Habtemichael N, Stauber RH (2006) EMBO Rep, 7:1259-65 PubMed
[2]. "Nuclear export is essential for the tumor-promoting activity of survivin."
Knauer SK, Kramer OH, Knosel T, Engels K, Rodel F, Kovacs AF, Dietmaier W, Klein-Hitpass L, Habtemichael N, Schweitzer A, Brieger J, Rodel C, Mann W, Petersen I, Heinzel T, Stauber RH (2007) FASEB J, 21:207-16 PubMed
[3]. "CRM1-mediated nuclear export determines the cytoplasmic localization of the antiapoptotic protein Survivin."
Rodriguez JA, Span SW, Ferreira CG, Kruyt FA, Giaccone G (2002) Exp Cell Res, 275:44-53 PubMed
[4]. "Separating the anti-apoptotic and mitotic roles of survivin."
Colnaghi R, Connell CM, Barrett RM, Wheatley SP (2006) J Biol Chem, 281:33450-6 PubMed
[5]. "Homodimerization antagonizes nuclear export of survivin."
Engelsma D, Rodriguez JA, Fish A, Giaccone G, Fornerod M (2007) Traffic, 8:1495-502 PubMed
Knauer SK, Bier C, Habtemichael N, Stauber RH (2006) EMBO Rep, 7:1259-65 PubMed
[2]. "Nuclear export is essential for the tumor-promoting activity of survivin."
Knauer SK, Kramer OH, Knosel T, Engels K, Rodel F, Kovacs AF, Dietmaier W, Klein-Hitpass L, Habtemichael N, Schweitzer A, Brieger J, Rodel C, Mann W, Petersen I, Heinzel T, Stauber RH (2007) FASEB J, 21:207-16 PubMed
[3]. "CRM1-mediated nuclear export determines the cytoplasmic localization of the antiapoptotic protein Survivin."
Rodriguez JA, Span SW, Ferreira CG, Kruyt FA, Giaccone G (2002) Exp Cell Res, 275:44-53 PubMed
[4]. "Separating the anti-apoptotic and mitotic roles of survivin."
Colnaghi R, Connell CM, Barrett RM, Wheatley SP (2006) J Biol Chem, 281:33450-6 PubMed
[5]. "Homodimerization antagonizes nuclear export of survivin."
Engelsma D, Rodriguez JA, Fish A, Giaccone G, Fornerod M (2007) Traffic, 8:1495-502 PubMed
User Input
Accurate identification of NESs is difficult because many sequences in the genome match the NES consensus.
Therefore, some published NESs may be mistakenly identified. Please help us improve the accuracy of NESdb
by providing either a positive or negative flag for the NES in this entry. Supporting comments are required to process the flag.