5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2
UniProt
Show FASTA Format
>gi|728758|sp|Q09137.1|AAPK2_RAT RecName: Full=5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2; Short=AMPK subunit alpha-2
MAEKQKHDGRVKIGHYVLGDTLGVGTFGKVKIGEHQLTGHKVAVKILNRQKIRSLDVVGKIKREIQNLKL
FRHPHIIKLYQVISTPTDFFMVMEYVSGGELFDYICKHGRVEEVEARRLFQQILSAVDYCHRHMVVHRDL
KPENVLLDAQMNAKIADFGLSNMMSDGEFLRTSCGSPNYAAPEVISGRLYAGPEVDIWSCGVILYALLCG
TLPFDDEHVPTLFKKIRGGVFYIPEYLNRSIATLLMHMLQVDPLKRATIKDIREHEWFKQDLPSYLFPED
PSYDANVIDDEAVKEVCEKFECTESEVMNSLYSGDPQDQLAVAYHLIIDNRRIMNQASEFYLASSPPTGS
FMDDMAMHIPPGLKPHPERMPPLIADSPKARCPLDALNTTKPKSLAVKKAKWHLGIRSQSKPYDIMAEVY
RAMKQLDFEWKVVNAYHLRVRRKNPVTGNYVKMSLQLYLVDNRSYLLDFKSIDDEVVEQRSGSSTPQRSC
SAAGLHRPRSSVDSSTAENHSLSGSLTGSLTGSTLSSASPRLGSHTMDFFEMCASLITALAR
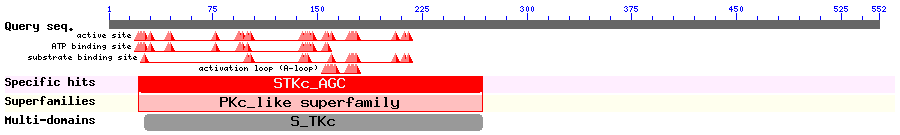
Show Domain Info by CDD
Show Secondary Structure by PSIPRED
# PSIPRED HFORMAT (PSIPRED V3.2)
Conf: 974446899701116122113413454202577741038568888630000001130357
Pred: CCCCCCCCCCEEECCCEEEEEEECCCCCCEEEEEEEECCCEEEEEEEEHHHHCCCCHHHH
AA: MAEKQKHDGRVKIGHYVLGDTLGVGTFGKVKIGEHQLTGHKVAVKILNRQKIRSLDVVGK
10 20 30 40 50 60
Conf: 899998642127984232478743697069998522477414763615754868999999
Pred: HHHHHHHHHHCCCCCEEEEEEEEECCCEEEEEEEECCCCCHHHHHHHCCCCCHHHHHHHH
AA: IKREIQNLKLFRHPHIIKLYQVISTPTDFFMVMEYVSGGELFDYICKHGRVEEVEARRLF
70 80 90 100 110 120
Conf: 999987532010320036899743001678981474036766667896300267999767
Pred: HHHHHHHHHHHCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCEEEEECCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
AA: QQILSAVDYCHRHMVVHRDLKPENVLLDAQMNAKIADFGLSNMMSDGEFLRTSCGSPNYA
130 140 150 160 170 180
Conf: 742014754578843200132665766625789999991788873506510369887967
Pred: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCHHHHHHHHHHCCCCCCCCCHHHHHHHHHCCCCCCCCCCCHH
AA: APEVISGRLYAGPEVDIWSCGVILYALLCGTLPFDDEHVPTLFKKIRGGVFYIPEYLNRS
190 200 210 220 230 240
Conf: 999996430359787768555630988553699998999998877878999999999982
Pred: HHHHHHHHCCCCCCCCCCHHHHHCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCHHHHHHHHHHC
AA: IATLLMHMLQVDPLKRATIKDIREHEWFKQDLPSYLFPEDPSYDANVIDDEAVKEVCEKF
250 260 270 280 290 300
Conf: 989899999874299998478999998851564301421112499999998899878999
Pred: CCCHHHHHHHHHCCCCCCHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
AA: ECTESEVMNSLYSGDPQDQLAVAYHLIIDNRRIMNQASEFYLASSPPTGSFMDDMAMHIP
310 320 330 340 350 360
Conf: 999999999998767999887888876789998764335334796505899899999999
Pred: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCEEEEEEECCCCHHHHHHHHH
AA: PGLKPHPERMPPLIADSPKARCPLDALNTTKPKSLAVKKAKWHLGIRSQSKPYDIMAEVY
370 380 390 400 410 420
Conf: 998655968867256117999857999962699999987628915897641684000146
Pred: HHHHHCCCEEEEECCCEEEEEEECCCCCCEEEEEEEEEEEECCCEEEEEEECCCHHCCCC
AA: RAMKQLDFEWKVVNAYHLRVRRKNPVTGNYVKMSLQLYLVDNRSYLLDFKSIDDEVVEQR
430 440 450 460 470 480
Conf: 899998766786688999988898743567888887787888987789999998730099
Pred: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCHHHH
AA: SGSSTPQRSCSAAGLHRPRSSVDSSTAENHSLSGSLTGSLTGSTLSSASPRLGSHTMDFF
490 500 510 520 530 540
Conf: 999999999709
Pred: HHHHHHHHHHCC
AA: EMCASLITALAR
550
Show Conservation Score by AL2CO
1 M -1.000 *
2 A -1.000 *
3 E -1.000 *
4 K -1.000 *
5 Q -1.000 *
6 K -1.000 *
7 H -1.000 *
8 D -1.000 *
9 G -1.000 *
10 R -0.869
11 V -0.747
12 K -0.665
13 I 0.769
14 G -0.314
15 H -0.741
16 Y 1.799
17 V -0.814
18 L 0.114
19 G -0.657
20 D -0.479
21 T -0.132
22 L 0.882
23 G 1.807
24 V -0.673
25 G 2.457
26 T 0.504
27 F 1.353
28 G 1.348
29 K -0.026
30 V 2.457
31 K 1.212
32 I -0.309
33 G 1.621
34 E -0.711
35 H 1.249
36 Q -0.872
37 L -0.793
38 T 0.942
39 G -0.073
40 H -0.668
41 K -0.529
42 V 2.061
43 A 2.457
44 V 0.839
45 K 2.457
46 I 0.251
47 L 0.766
48 N 0.081
49 R 1.178
50 Q -0.472
51 K -0.441
52 I 0.841
53 R -0.650
54 S -0.837
55 L -0.877
56 D -0.441
57 V -0.047
58 V -0.779
59 G -0.777
60 K 1.286
61 I 0.696
62 K -0.736
63 R 1.621
64 E 2.457
65 I 0.733
66 Q -0.586
67 N 0.110
68 L 0.708
69 K 0.143
70 L -0.745
71 F 0.322
72 R -0.650
73 H 2.047
74 P 0.633
75 H 1.392
76 I 1.398
77 I 0.607
78 K 0.485
79 L 0.767
80 Y 0.560
81 Q 0.388
82 V 0.940
83 I 0.434
84 S -0.637
85 T 0.414
86 P -0.559
87 T -0.607
88 D -0.333
89 F 0.475
90 F 0.283
91 M 0.612
92 V 0.999
93 M 0.195
94 E 2.457
95 Y 0.771
96 V 0.270
97 S -0.574
98 G -0.411
99 G -0.031
100 E 1.792
101 L 0.952
102 F 1.464
103 D 0.204
104 Y 0.133
105 I 1.652
106 C -0.094
107 K -0.547
108 H -0.325
109 G -0.159
110 R 0.096
111 V 0.240
112 E -0.717
113 E 0.117
114 V -0.711
115 E -0.249
116 A 0.912
117 R 0.369
118 R -0.744
119 L -0.249
120 F 1.125
121 Q -0.145
122 Q 1.703
123 I 0.559
124 L 0.533
125 S -0.322
126 A 0.997
127 V 0.623
128 D -0.143
129 Y 0.484
130 C 0.614
131 H 1.684
132 R -0.826
133 H -0.389
134 M -0.461
135 V 1.398
136 V 0.249
137 H 1.668
138 R 2.025
139 D 2.025
140 L 1.524
141 K 1.666
142 P 0.696
143 E 2.025
144 N 2.025
145 V 0.665
146 L 1.992
147 L 0.862
148 D 0.742
149 A -0.957
150 Q -0.578
151 M -0.695
152 N -0.382
153 A 0.731
154 K 1.564
155 I 0.981
156 A 0.033
157 D 2.025
158 F 1.221
159 G 2.457
160 L 1.158
161 S 0.930
162 N 1.428
163 M -0.812
164 M -0.302
165 S -0.860
166 D -0.528
167 G 1.350
168 E -0.775
169 F -0.466
170 L 1.612
171 R -0.262
172 T 2.082
173 S 0.088
174 C 2.068
175 G 2.068
176 S 1.396
177 P 0.902
178 N 0.676
179 Y 2.457
180 A 1.118
181 A 1.239
182 P 2.457
183 E 1.762
184 V 0.935
185 I 0.707
186 S -0.376
187 G 0.577
188 R -0.308
189 L -0.775
190 Y 2.071
191 A -0.658
192 G 1.443
193 P 0.302
194 E -0.254
195 V 0.564
196 D 2.066
197 I 0.802
198 W 2.457
199 S 2.457
200 C 0.265
201 G 2.068
202 V 1.471
203 I 1.412
204 L 1.233
205 Y 1.417
206 A 0.842
207 L 0.666
208 L 0.443
209 C 0.294
210 G 0.975
211 T -0.446
212 L 1.514
213 P 1.750
214 F 1.750
215 D 0.818
216 D 0.148
217 E -0.522
218 H -0.451
219 V 0.241
220 P -0.551
221 T -0.659
222 L 1.630
223 F 0.024
224 K -0.355
225 K 0.733
226 I 1.217
227 R -0.704
228 G -0.645
229 G 1.249
230 V -0.833
231 F 1.191
232 Y -0.822
233 I -0.080
234 P 1.755
235 E -0.848
236 Y -0.112
237 L 0.194
238 N -0.292
239 R -0.836
240 S -0.678
241 I 0.002
242 A -0.395
243 T -0.703
244 L 0.926
245 L 1.057
246 M -0.697
247 H -0.548
248 M 0.514
249 L 1.785
250 Q -0.661
251 V 0.143
252 D 0.566
253 P 0.961
254 L -0.660
255 K -0.478
256 R 2.089
257 A -0.400
258 T -0.155
259 I 0.268
260 K -0.640
261 D -0.469
262 I 0.115
263 R -0.555
264 E -0.762
265 H -0.038
266 E -0.584
267 W 1.547
268 F 0.167
269 K -0.552
270 Q -0.862
271 D -0.790
272 L -0.844
273 P -0.365
274 S -0.866
275 Y -0.869
276 L -0.727
277 F -1.051
278 P -0.960
279 E -1.047
280 D -1.068
281 P -0.997
282 S -1.055
283 Y -1.095
284 D -0.899
285 A -1.032
286 N -0.876
287 V -1.008
288 I -0.688
289 D -0.736
290 D -0.859
291 E -0.800
292 A -0.868
293 V -0.312
294 K -0.878
295 E -0.860
296 V -0.759
297 C -0.759
298 E -0.775
299 K -0.884
300 F -0.505
301 E -0.653
302 C -0.595
303 T -0.826
304 E -0.792
305 S -0.856
306 E -0.813
307 V -0.273
308 M -1.001
309 N -0.942
310 S -0.594
311 L -0.292
312 Y -1.022
313 S -0.818
314 G -0.912
315 D -0.758
316 P -0.954
317 Q -0.924
318 D -0.161
319 Q -0.854
320 L -0.458
321 A -0.715
322 V -0.348
323 A -0.266
324 Y 0.702
325 H -0.822
326 L 1.346
327 I -0.057
328 I -0.767
329 D -0.153
330 N -0.370
331 R -0.654
332 R -0.842
333 I -1.014
334 M -0.905
335 N -0.995
336 Q -0.891
337 A -1.059
338 S -0.899
339 E -0.748
340 F -1.082
341 Y -0.927
342 L -0.981
343 A -0.937
344 S -0.838
345 S -0.936
346 P -1.079
347 P -1.021
348 T -1.041
349 G -1.087
350 S -0.997
351 F -1.075
352 M -0.988
353 D -0.984
354 D -0.989
355 M -1.047
356 A -1.018
357 M -1.076
358 H -0.988
359 I -0.951
360 P -0.978
361 P -0.862
362 G -0.941
363 L -1.052
364 K -1.009
365 P -0.949
366 H -1.030
367 P -0.974
368 E -0.928
369 R -0.944
370 M -1.025
371 P -0.875
372 P -0.828
373 L -0.965
374 I -1.034
375 A -1.050
376 D -0.995
377 S -1.016
378 P -0.987
379 K -0.994
380 A -1.022
381 R -1.098
382 C -1.022
383 P -0.899
384 L -0.975
385 D -0.966
386 A -1.006
387 L -1.037
388 N -0.948
389 T -1.012
390 T -1.021
391 K -1.062
392 P -0.939
393 K -0.963
394 S -0.948
395 L -0.980
396 A -0.979
397 V -0.941
398 K -0.781
399 K -0.902
400 A -0.873
401 K -0.670
402 W -0.763
403 H -0.918
404 L -0.404
405 G -0.022
406 I -0.559
407 R -0.588
408 S -0.785
409 Q -0.740
410 S -0.776
411 K -0.759
412 P 0.023
413 Y -0.995
414 D -0.430
415 I 0.126
416 M -0.031
417 A -0.880
418 E -0.283
419 V 0.706
420 Y -0.190
421 R -0.534
422 A -0.065
423 M 0.521
424 K -0.699
425 Q -1.000 *
426 L -1.000 *
427 D -1.000 *
428 F -1.000 *
429 E -1.000 *
430 W -1.000 *
431 K -1.000 *
432 V -1.000 *
433 V -1.000 *
434 N -1.000 *
435 A -1.000 *
436 Y -1.000 *
437 H -1.000 *
438 L -1.000 *
439 R -1.000 *
440 V -1.000 *
441 R -1.000 *
442 R -1.000 *
443 K -1.000 *
444 N -1.000 *
445 P -1.000 *
446 V -1.000 *
447 T -1.000 *
448 G -1.000 *
449 N -1.000 *
450 Y -1.000 *
451 V -1.000 *
452 K -1.000 *
453 M -1.000 *
454 S -1.000 *
455 L -1.000 *
456 Q -1.000 *
457 L -1.000 *
458 Y -1.000 *
459 L -1.000 *
460 V -1.000 *
461 D -1.000 *
462 N -1.000 *
463 R -1.000 *
464 S -1.000 *
465 Y -1.000 *
466 L -1.000 *
467 L -1.000 *
468 D -1.000 *
469 F -1.000 *
470 K -1.000 *
471 S -1.000 *
472 I -1.000 *
473 D -1.000 *
474 D -1.000 *
475 E -1.000 *
476 V -1.000 *
477 V -1.000 *
478 E -1.000 *
479 Q -1.000 *
480 R -1.000 *
481 S -1.000 *
482 G -1.000 *
483 S -1.000 *
484 S -1.000 *
485 T -1.000 *
486 P -1.000 *
487 Q -1.000 *
488 R -1.000 *
489 S -1.000 *
490 C -1.000 *
491 S -1.000 *
492 A -1.000 *
493 A -1.000 *
494 G -1.000 *
495 L -1.000 *
496 H -1.000 *
497 R -1.000 *
498 P -1.000 *
499 R -1.000 *
500 S -1.000 *
501 S -1.000 *
502 V -1.000 *
503 D -1.000 *
504 S -1.000 *
505 S -1.000 *
506 T -1.000 *
507 A -1.000 *
508 E -1.000 *
509 N -1.000 *
510 H -1.000 *
511 S -1.000 *
512 L -1.000 *
513 S -1.000 *
514 G -1.000 *
515 S -1.000 *
516 L -1.000 *
517 T -1.000 *
518 G -1.000 *
519 S -1.000 *
520 L -1.000 *
521 T -1.000 *
522 G -1.000 *
523 S -1.000 *
524 T -1.000 *
525 L -1.000 *
526 S -1.000 *
527 S -1.000 *
528 A -1.000 *
529 S -1.000 *
530 P -1.000 *
531 R -1.000 *
532 L -1.000 *
533 G -1.000 *
534 S -1.000 *
535 H -1.000 *
536 T -1.000 *
537 M -1.000 *
538 D -1.000 *
539 F -1.000 *
540 F -1.000 *
541 E -1.000 *
542 M -1.000 *
543 C -1.000 *
544 A -1.000 *
545 S -1.000 *
546 L -1.000 *
547 I -1.000 *
548 T -1.000 *
549 A -1.000 *
550 L -1.000 *
551 A -1.000 *
552 R -1.000 *
* gap fraction no less than 0.50; conservation set to M-S
M: mean; S: standard deviation
al2co - The parameters are:
Input alignment file - 156.paln
Output conservation - STDOUT
Weighting scheme - independent-count based
Conservation calculation method - entropy-based
Window size - 1
Conservation normalized to zero mean and unity variance
Gap fraction to suppress calculation - 0.50
10 20 30 40 50 60
MAEKQKHDGR VKIGHYVLGD TLGVGTFGKV KIGEHQLTGH KVAVKILNRQ KIRSLDVVGK
70 80 90 100 110 120
IKREIQNLKL FRHPHIIKLY QVISTPTDFF MVMEYVSGGE LFDYICKHGR VEEVEARRLF
130 140 150 160 170 180
QQILSAVDYC HRHMVVHRDL KPENVLLDAQ MNAKIADFGL SNMMSDGEFL RTSCGSPNYA
190 200 210 220 230 240
APEVISGRLY AGPEVDIWSC GVILYALLCG TLPFDDEHVP TLFKKIRGGV FYIPEYLNRS
250 260 270 280 290 300
IATLLMHMLQ VDPLKRATIK DIREHEWFKQ DLPSYLFPED PSYDANVIDD EAVKEVCEKF
310 320 330 340 350 360
ECTESEVMNS LYSGDPQDQL AVAYHLIIDN RRIMNQASEF YLASSPPTGS FMDDMAMHIP
370 380 390 400 410 420
PGLKPHPERM PPLIADSPKA RCPLDALNTT KPKSLAVKKA KWHLGIRSQS KPYDIMAEVY
430 440 450 460 470 480
RAMKQLDFEW KVVNAYHLRV RRKNPVTGNY VKMSLQLYLV DNRSYLLDFK SIDDEVVEQR
490 500 510 520 530 540
SGSSTPQRSC SAAGLHRPRS SVDSSTAENH SLSGSLTGSL TGSTLSSASP RLGSHTMDFF
550
EMCASLITAL AR
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation targets are found both in the nucleus and cytoplasm and is activated by cellular stressors such as heat shock, low energy levels, and oxidative stress. AMPK restores energetic balance by inhibiting anabolic processes that consume energy and enabling catabolic pathways that produce cellular energy. Nuclear targets of AMPK include PGC1α and
PPARα/β/γ that regulate transcription in the nucleus.
Consisting of a trimer containing catalytic serine-threonine kinase subunit α and two regulatory subunits β and γ, the NES in the carboxy-terminal of AMPKα provides an additional mechanism for AMPK regulation. While not required for binding with the β and γ subunits, the carboxy terminus in AMPKα is necessary for nuclear export. In vivo experiments have also shown the 22 amino acids to be crucial for Drosophila neuronal maintenance and viability as well as normal localization. Truncated AMPKα also exhibit reduced phosphorylation due to the cytoplasmic localization needed for LKB1, an upstream activator.
[1]. "Identification of a Nuclear Export Signal in the Catalytic Subunit of AMP-activated Protein Kinase"
Kazgan N, Williams T, Forsberg LJ, Brenman JE. (2010)
Mol Biol Cell,
21:3433-42
PubMed
Accurate identification of NESs is difficult because many sequences in the genome match the NES consensus.
Therefore, some published NESs may be mistakenly identified. Please help us improve the accuracy of NESdb
by providing either a positive or negative flag for the NES in this entry. Supporting comments are required to process the flag.
