Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX6
UniProt
*shown as underlined residues in the full sequence
1MSTARTENPVLMGMSSQNGQLRGPLKPSAGPGGGGTQTQQINQLKNASTINSGSQQQAQS
MSSIIKPGDDWKKTLKLPPKDLRIKTSDVTSTKGNEFEDYCLKRELLMGIFEMGWEKPSP
IQEESIPIALSGRDILARAKNGTGKTGAYLIPLLERLDLKKDCI
164 Ref.1RNA helicase p54 (DDX6) is a shuttling protein involved in nuclear assembly of stored mRNP particles, Smillie et al., J Cell Sci, 2001
Show FASTA Format
>gi|288558810|sp|P54824.2|DDX6_XENLA RecName: Full=ATP-dependent RNA helicase ddx6; AltName: Full=ATP-dependent RNA helicase p54; Short=P54H; Short=Xp54; AltName: Full=DEAD box protein 6
MSTARTENPVLMGMSSQNGQLRGPLKPSAGPGGGGTQTQQINQLKNASTINSGSQQQAQSMSSIIKPGDD
WKKTLKLPPKDLRIKTSDVTSTKGNEFEDYCLKRELLMGIFEMGWEKPSPIQEESIPIALSGRDILARAK
NGTGKSGAYLIPLLERLDLKKDCIQAMVIVPTRELALQVSQICIQVSKHMGGAKVMATTGGTNLRDDIMR
LDDTVHVVIATPGRILDLIKKGVAKVDHIQMIVLDEADKLLSQDFMQIMEDIIMTLPKNRQILLYSATFP
LSVQKFMTLHLQKPYEINLMEELTLKGVTQYYAYVTERQKVHCLNTLFSRLQINQSIIFCNSSQRVELLA
KKISQLGYSCFYIHAKMRQEHRNRVFHDFRNGLCRNLVCTDLFTRGIDIQAVNVVINFDFPKLAETYLHR
IGRSGRFGHLGLAINLITYDDRFNLKSIEEQLGTEIKPIPSSIDKNLYVAEYHSESGEDKP
Show Domain Info by CDD
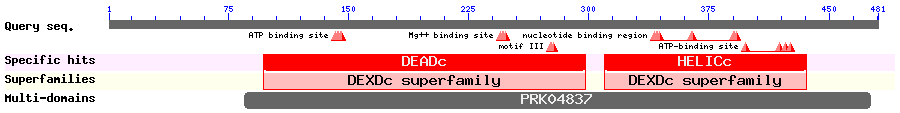
Show Secondary Structure by PSIPRED
# PSIPRED HFORMAT (PSIPRED V3.2)
Conf: 986555698111244677843389999999999998752544202567678774001123
Pred: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCHHHHHHCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
AA: MSTARTENPVLMGMSSQNGQLRGPLKPSAGPGGGGTQTQQINQLKNASTINSGSQQQAQS
10 20 30 40 50 60
Conf: 456789995100027999988873132000146885433352178875563304778982
Pred: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCEECCCCCCCCCCCCHHHHHHHHHHHCCCCCCC
AA: MSSIIKPGDDWKKTLKLPPKDLRIKTSDVTSTKGNEFEDYCLKRELLMGIFEMGWEKPSP
70 80 90 100 110 120
Conf: 000110001036233333247998511344001111379987200799622368878999
Pred: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCEEEECCCCCCCCEEEECHHHHHCCCCCCCEEEEEECCCHHHHHHHH
AA: IQEESIPIALSGRDILARAKNGTGKSGAYLIPLLERLDLKKDCIQAMVIVPTRELALQVS
130 140 150 160 170 180
Conf: 999998511398079993099872676763069746998289233530026975358955
Pred: HHHHHHHCCCCCCEEEEECCCCCHHHHHHHHCCCCEEEECCCCHHHHHCCCCCCCCCCCC
AA: QICIQVSKHMGGAKVMATTGGTNLRDDIMRLDDTVHVVIATPGRILDLIKKGVAKVDHIQ
190 200 210 220 230 240
Conf: 588313000169233999999997299985399995035420898886623798367503
Pred: EEEEECCCCCCCHHHHHHHHHHHHHCCCCCEEEEEECCCCCHHHHHHHHHCCCCEEEEEC
AA: MIVLDEADKLLSQDFMQIMEDIIMTLPKNRQILLYSATFPLSVQKFMTLHLQKPYEINLM
250 260 270 280 290 300
Conf: 443235410677875202102235543200012205997337226899998745229323
Pred: CCCCCCCEEEEEEEEECCCHHHHHHHHHHCCCCCEEEEEECCCHHHHHHHHHHHHCCCEE
AA: EELTLKGVTQYYAYVTERQKVHCLNTLFSRLQINQSIIFCNSSQRVELLAKKISQLGYSC
310 320 330 340 350 360
Conf: 665044352101223230246973035521432355533014799822699994200000
Pred: EEECCCCCCHHHHHHHHHCCCCCCEEEEECCCCCCCCCCCEEEEEEECCCCCCCCCCHHC
AA: FYIHAKMRQEHRNRVFHDFRNGLCRNLVCTDLFTRGIDIQAVNVVINFDFPKLAETYLHR
370 380 390 400 410 420
Conf: 257888886205773035121211999988867954337866665302310589989999
Pred: CCCCCCCCCCCEEEEECCHHHHCCHHHHHHHHCCCCCCCCCCCCCCEEEECCCCCCCCCC
AA: IGRSGRFGHLGLAINLITYDDRFNLKSIEEQLGTEIKPIPSSIDKNLYVAEYHSESGEDK
430 440 450 460 470 480
Conf: 9
Pred: C
AA: P
Show Conservation Score by AL2CO
1 M -1.000 *
2 S -1.000 *
3 T -1.000 *
4 A -1.000 *
5 R -1.000 *
6 T -1.000 *
7 E -1.000 *
8 N -1.000 *
9 P -1.000 *
10 V -1.000 *
11 L -1.000 *
12 M -1.000 *
13 G -1.000 *
14 M -1.000 *
15 S -1.000 *
16 S -1.000 *
17 Q -1.000 *
18 N -1.000 *
19 G -1.000 *
20 Q -1.000 *
21 L -1.000 *
22 R -1.000 *
23 G -1.000 *
24 P -1.000 *
25 L -1.000 *
26 K -1.000 *
27 P -1.000 *
28 S -1.000 *
29 A -1.000 *
30 G -1.000 *
31 P -1.000 *
32 G -1.000 *
33 G -1.000 *
34 G -1.000 *
35 G -1.000 *
36 T -1.000 *
37 Q -1.000 *
38 T -1.000 *
39 Q -1.000 *
40 Q -1.000 *
41 I -1.000 *
42 N -1.000 *
43 Q -1.000 *
44 L -1.000 *
45 K -1.000 *
46 N -1.000 *
47 A -1.000 *
48 S -1.000 *
49 T -1.000 *
50 I -1.000 *
51 N -1.000 *
52 S -1.000 *
53 G -1.000 *
54 S -1.000 *
55 Q -1.000 *
56 Q -1.000 *
57 Q -1.000 *
58 A -1.000 *
59 Q -1.000 *
60 S -1.000 *
61 M -1.000 *
62 S -1.000 *
63 S -1.000 *
64 I -1.000 *
65 I -1.000 *
66 K -1.000 *
67 P -1.000 *
68 G -1.000 *
69 D -1.000 *
70 D -1.000 *
71 W -1.000 *
72 K -1.000 *
73 K -1.000 *
74 T -1.000 *
75 L -1.000 *
76 K -1.000 *
77 L -1.000 *
78 P -1.000 *
79 P -1.000 *
80 K -1.000 *
81 D -1.000 *
82 L -1.000 *
83 R -1.000 *
84 I -1.000 *
85 K -1.000 *
86 T -1.000 *
87 S -1.000 *
88 D -1.000 *
89 V -1.103
90 T -1.099
91 S -1.054
92 T -0.854
93 K -1.091
94 G -1.222
95 N -1.232
96 E -0.767
97 F 1.637
98 E -0.971
99 D -0.518
100 Y 0.072
101 C -1.124
102 L 0.323
103 K -1.114
104 R -0.831
105 E -1.029
106 L 0.314
107 L -0.799
108 M -0.743
109 G 0.362
110 I 0.472
111 F -1.213
112 E -0.784
113 M -0.793
114 G 1.634
115 W 0.675
116 E 0.558
117 K -0.983
118 P 0.451
119 S 1.281
120 P 0.574
121 I 1.393
122 Q 2.090
123 E -0.704
124 E -0.735
125 S -0.047
126 I 0.722
127 P -0.754
128 I -1.113
129 A -0.696
130 L -0.267
131 S -1.007
132 G 0.030
133 R -1.099
134 D 0.827
135 I 0.140
136 L 0.284
137 A 0.758
138 R 0.163
139 A 1.457
140 K 1.069
141 N 0.802
142 G 1.721
143 T 1.616
144 G 1.721
145 K 2.090
146 S 1.494
147 G 0.349
148 A 0.092
149 Y 0.786
150 L -0.321
151 I 0.284
152 P 0.245
153 L -0.428
154 L 0.216
155 E -0.613
156 R -1.013
157 L -0.068
158 D -0.512
159 L -1.328
160 K -0.896
161 K -1.324
162 D -1.241
163 C -1.338
164 I -0.230
165 Q 0.342
166 A -0.508
167 M 0.219
168 V 0.087
169 I 0.538
170 V -0.260
171 P 1.722
172 T 1.721
173 R 2.090
174 E 2.090
175 L 2.090
176 A 1.111
177 L -0.637
178 Q 2.090
179 V -0.203
180 S -0.588
181 Q -0.748
182 I -0.426
183 C -0.427
184 I -1.253
185 Q -0.909
186 V 0.046
187 S -0.089
188 K -1.039
189 H -0.818
190 M -0.998
191 G -0.870
192 G -0.865
193 A -0.323
194 K -0.839
195 V -0.316
196 M -0.617
197 A -0.283
198 T -0.222
199 T 0.194
200 G 2.090
201 G 1.721
202 T -0.410
203 N -1.065
204 L 0.012
205 R -0.956
206 D -1.089
207 D 1.004
208 I -0.211
209 M -0.915
210 R -1.040
211 L 0.730
212 D -0.929
213 D -1.094
214 T -0.817
215 V -0.185
216 H 0.047
217 V 0.223
218 V 0.443
219 I 0.303
220 A 1.076
221 T 2.090
222 P 2.090
223 G 2.090
224 R 2.090
225 I 0.031
226 L -0.720
227 D 1.614
228 L 0.603
229 I -0.280
230 K -0.772
231 K 0.749
232 G -0.430
233 V -0.843
234 A -0.005
235 K -0.890
236 V -0.449
237 D -0.702
238 H -1.114
239 I -0.198
240 Q -1.001
241 M -0.902
242 I -0.233
243 V 0.249
244 L 0.712
245 D 2.090
246 E 2.090
247 A 0.921
248 D 2.090
249 K 0.735
250 L 1.290
251 L 1.405
252 S -0.464
253 Q -0.977
254 D 0.509
255 F 1.028
256 M -0.853
257 Q -0.824
258 I -0.580
259 M 0.209
260 E -0.644
261 D -1.238
262 I 0.321
263 I 0.036
264 M -1.019
265 T -1.285
266 L -0.533
267 P -0.353
268 K -1.114
269 N -0.899
270 R -0.567
271 Q 1.175
272 I -0.359
273 L -0.543
274 L 0.418
275 Y 0.196
276 S 2.090
277 A 2.090
278 T 2.090
279 F 0.115
280 P 0.609
281 L -1.384
282 S -1.016
283 V 0.990
284 Q -0.985
285 K -0.891
286 F 0.162
287 M -0.548
288 T -0.943
289 L -0.784
290 H -0.132
291 L 0.121
292 Q -0.920
293 K -0.644
294 P 0.241
295 Y -1.012
296 E -1.161
297 I 0.486
298 N -0.721
299 L 0.459
300 M -0.793
301 E -0.804
302 E -0.295
303 L -0.760
304 T 1.120
305 L -0.332
306 K -0.949
307 G -0.785
308 V 0.549
309 T -0.633
310 Q 1.334
311 Y -1.020
312 Y 0.622
313 A -0.577
314 Y -1.361
315 V -0.302
316 T -1.190
317 E -0.739
318 R -1.293
319 Q -1.304
320 K 1.301
321 V -0.849
322 H 0.105
323 C -0.397
324 L 0.359
325 N -0.057
326 T 0.244
327 L 0.203
328 F -0.407
329 S -0.452
330 R -0.870
331 L -0.907
332 Q -0.910
333 I -0.684
334 N -0.811
335 Q -0.225
336 S -0.412
337 I 0.565
338 I 0.344
339 F 1.563
340 C -0.164
341 N 0.687
342 S 1.313
343 S -0.124
344 Q -0.842
345 R -0.956
346 V 0.476
347 E -0.575
348 L -0.901
349 L 0.715
350 A -0.496
351 K -1.000
352 K -1.055
353 I 0.508
354 S -1.051
355 Q -1.018
356 L -0.554
357 G 0.304
358 Y -0.016
359 S -1.130
360 C 0.150
361 F -0.872
362 Y -0.650
363 I 0.172
364 H 0.994
365 A 0.916
366 K -0.088
367 M 0.392
368 R -1.185
369 Q 1.723
370 E -1.185
371 H -1.023
372 R 2.090
373 N -0.297
374 R -0.983
375 V 0.349
376 F 0.070
377 H -0.766
378 D -0.786
379 F 0.781
380 R 0.659
381 N -0.895
382 G 0.073
383 L -1.211
384 C -0.623
385 R 0.091
386 N -0.481
387 L 0.869
388 V 1.035
389 C 0.179
390 T 1.338
391 D 2.090
392 L 0.867
393 F 0.069
394 T 0.700
395 R 1.721
396 G 2.090
397 I 1.038
398 D 1.722
399 I 1.014
400 Q -0.669
401 A -0.669
402 V 0.800
403 N 0.058
404 V -0.338
405 V 1.680
406 I 0.087
407 N 1.615
408 F 1.255
409 D 1.692
410 F 0.117
411 P 2.090
412 K -1.159
413 L -0.725
414 A -0.811
415 E 0.927
416 T -0.555
417 Y 2.090
418 L 0.572
419 H 2.090
420 R 2.090
421 I 1.438
422 G 2.090
423 R 2.090
424 S 0.700
425 G 1.630
426 R 2.090
427 F 0.642
428 G 1.715
429 H -0.087
430 L -1.171
431 G 2.090
432 L -1.059
433 A 1.079
434 I -0.170
435 N 0.159
436 L 0.670
437 I 0.095
438 T -0.922
439 Y -1.274
440 D -0.503
441 D 0.793
442 R -0.910
443 F -1.288
444 N -1.244
445 L 0.416
446 K -0.950
447 S -1.182
448 I 0.510
449 E 0.523
450 E -0.754
451 Q -0.983
452 L -0.494
453 G -0.888
454 T -0.795
455 E -1.006
456 I 0.195
457 K -1.159
458 P -0.737
459 I 0.046
460 P 0.175
461 S -0.994
462 S -1.218
463 I -1.027
464 D -0.367
465 K -0.840
466 N -1.001
467 L -0.848
468 Y -1.000 *
469 V -1.000 *
470 A -1.000 *
471 E -1.000 *
472 Y -1.000 *
473 H -1.000 *
474 S -1.000 *
475 E -1.000 *
476 S -1.000 *
477 G -1.000 *
478 E -1.000 *
479 D -1.000 *
480 K -1.000 *
481 P -1.000 *
* gap fraction no less than 0.50; conservation set to M-S
M: mean; S: standard deviation
al2co - The parameters are:
Input alignment file - 52.paln
Output conservation - STDOUT
Weighting scheme - independent-count based
Conservation calculation method - entropy-based
Window size - 1
Conservation normalized to zero mean and unity variance
Gap fraction to suppress calculation - 0.50
10 20 30 40 50 60
MSTARTENPV LMGMSSQNGQ LRGPLKPSAG PGGGGTQTQQ INQLKNASTI NSGSQQQAQS
70 80 90 100 110 120
MSSIIKPGDD WKKTLKLPPK DLRIKTSDVT STKGNEFEDY CLKRELLMGI FEMGWEKPSP
130 140 150 160 170 180
IQEESIPIAL SGRDILARAK NGTGKTGAYL IPLLERLDLK KDCIQAMVIV PTRELALQVS
190 200 210 220 230 240
QICIQVSKHM GGAKVMATTG GTNLRDDIMR LDDTVHVVIA TPGRILDLIK KGVAKVDHIQ
250 260 270 280 290 300
MIVLDEADKL LSQDFMQIME DIIMTLPKNR QILLYSATFP LSVQKFMTLH LQKPYEINLM
310 320 330 340 350 360
EELTLKGVTQ YYAYVTERQK VHCLNTLFSR LQINQSIIFC NSSQRVELLA KKISQLGYSC
370 380 390 400 410 420
FYIHAKMRQE HRNRVFHDFR NGLCRNLVCT DLFTRGIDIQ AVNVVINFDF PKLAETYLHR
430 440 450 460 470 480
IGRSGRFGHL GLAINLITYD DRFNLKSIEE QLGTEIKPIP SSIDKNLYVA EYHSESGEDK
P
Xp54 is one of the four proteins in a core group, abundant during early development of cells to maintain the mRNA sequences in a condition ready for translate at the appropriate stage of development. Xp54 is an ATP-dependent RNA helicase, belonging to a small family (DDX6) of DEAD-box RNA helicases. Smillie and Sommerville found that Xp54 is present in the oocyte nuclei and is able to shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. They showed that the N-terminal part of Xp54 (aa 1-164) can cause GFP to accumulate in the cytoplasm, which can be inhibited by LMB. Mutating L157 and L159 to alanine has similar effect. However, the full length protein doesn't respond to LMB treatment. In addition, replacement of the C-terminal 82 resiudes with an unrelated plasmid will make the recombinant protein responsive to LMB, suggesting that the C-terminal part harbors a cytoplasmic retention signal. More recently, Hwang et al. also illustrated that DDX6 is not LMB sensitive and is instead exported in a piggyback manner by 4E-T.
Ref.2Dual Mechanisms Regulate the Nucleocytoplasmic Localization of Human DDX6, Huang et al., Sci Rep, 2017
[1]. "RNA helicase p54 (DDX6) is a shuttling protein involved in nuclear assembly of stored mRNP particles"
Smillie, D.A., Sommerville, J. (2001)
J Cell Sci,
115:395-407
PubMed[2]. "Dual Mechanisms Regulate the Nucleocytoplasmic Localization of Human DDX6"
Huang JH, Ku WC, Chen YC, Chang YL, Chu CY. (2017)
Sci Rep,
7:42853
PubMed
Accurate identification of NESs is difficult because many sequences in the genome match the NES consensus.
Therefore, some published NESs may be mistakenly identified. Please help us improve the accuracy of NESdb
by providing either a positive or negative flag for the NES in this entry. Supporting comments are required to process the flag.
