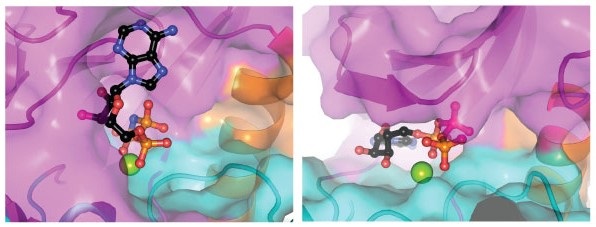
Distant Protein Kinase homolog SelO function as an AMPylator. Surface representations illustrating the orientation of the nucleotide in the active site of P.syringae SelO (left) and in the active site of a typical protein kinase CK1 (right), with the N-lobe colored magenta, the C-lobe colored cyan, and the αC helix is in orange. The ATP is flipped in SelO to allow transfer of AMP to protein substrates.