Databases
Grishin Lab Databases
-
ECOD
-
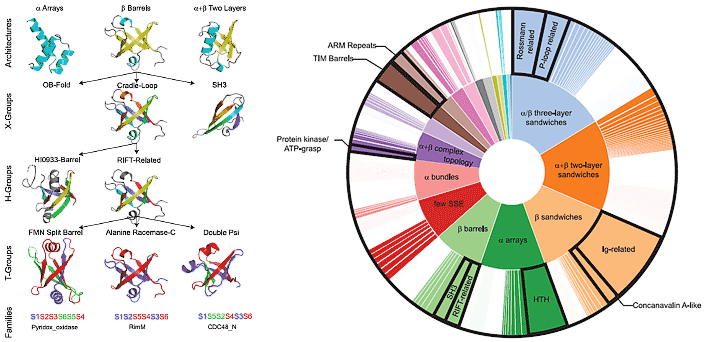
Evolutionary Classification of Protein Domains
ECOD is a hierarchical classification of protein domains according to their evolutionary relationships.ECOD is updated weekly by a combination of automtic methods and manual curation.
Reference: H. Cheng, R. D. Schaeffer, Y. Liao, L. N. Kinch, J. Pei, S. Shi, B. H. Kim, N. V. Grishin. (2014) "ECOD: An evolutionary classification of protein domains". PloS Computational Biology 10(12): e1003926 PMID: 25474468
-
M2SG
-
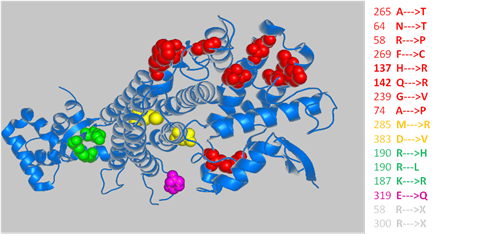
From curated clinical Mutations to protein Sequences and Genomic loci.
This is a database mapping human disease-related genetic variants to protein sequences and genomic loci.Reference: Ji R, Cong Q, Li W, Grishin NV. (2013) "M2SG: Mapping Human Disease-Related Genetic Variants to Protein Sequences and Genomic Loci". Bioinformatics 29(22): 2953-2954 PMID: 24002112
-
PALas
-
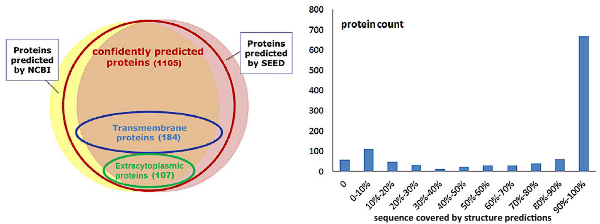
Predictive Analysis of Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus proteome.
This is a website that contains predictive information for every protein from Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus, the pathogen for the Citrus Greening disease.Reference: Q.Cong, L.N.Kinch, B.H.Kim, N.V.Grishin. (2012) "Predictive sequence analysis of the Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus proteome". PLoS ONE 7(7): e41071 PMID: 22815919
-
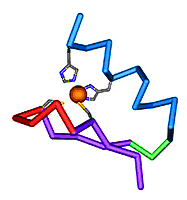
Structural Classification of Zinc Fingers
-
Zinc fingers are small protein domains in which zinc plays a structural role contributing to the stability of the domain. Zinc fingers are structurally diverse and are present among proteins that perform a broad range of functions in various cellular processes. Zinc fingers typically function as interaction modules and bind to a wide variety of compounds, such as nucleic acids, proteins and small molecules.
We have made a comprehensive classification of zinc finger spatial structures. The zinc finger database has been constructed by manual examination of zinc finger domain structures. We find that each available zinc finger structure can be placed into one of eight fold groups that we define based on the structural properties in the vicinity of the zinc-binding site. Evolutionary relatedness of proteins within fold groups is not implied, but each group is divided into families of potential homologues.
Reference: S.S.Krishna, I.Majumdar, and N.V.Grishin (2003) "Structural classification of zinc fingers". Nucleic Acid Research 31(2): 532-550 PMID: 12527760
-
MALIDUP
-
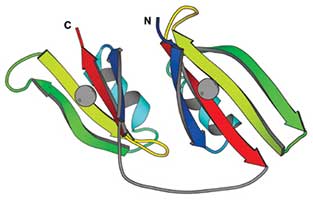
Manual ALIgnments of DUPlicated domains.
A database of pairwise, structure-base alignments for homologous domains originated by internal duplication.Reference: H.Cheng, B.H.Kim, and N.V.Grishin (2007) "MALIDUP: a database of manually constructed structure alignments for duplicated domain pairs". Proteins 70(4): 1162-1166 PMID: 17932926
-
MALISAM
-
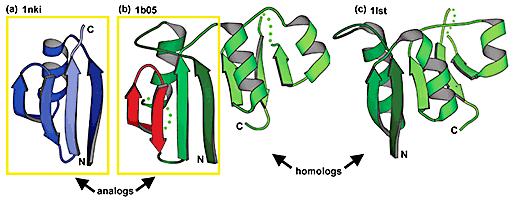
Manual ALIgnments of Structurally Analogous Motifs.
A database of pairwise, structure-based alignments for structurally analogous but evolutionarily unrelated motifs in proteins.Reference: H.Cheng, B.H.Kim, and N.V.Grishin (2007) "MALISAM: a database of structurally analogous motifs". Nucleic Acids 36(Database Issue): D211-217 PMID: 17855399
-
MultiDom
-
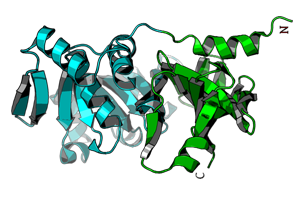
MultiDomain proteins.
A database of domain definitions for Multidomain protein class in SCOPReference: I.Majumdar, L.N.Kinch, and N.V.Grishin (2009) "A database of domain definitions for proteins with complex interdomain geometry." PLoS ONE 4(4): e5084 Apr 8; PMID: 19352501